What is a whiplash?
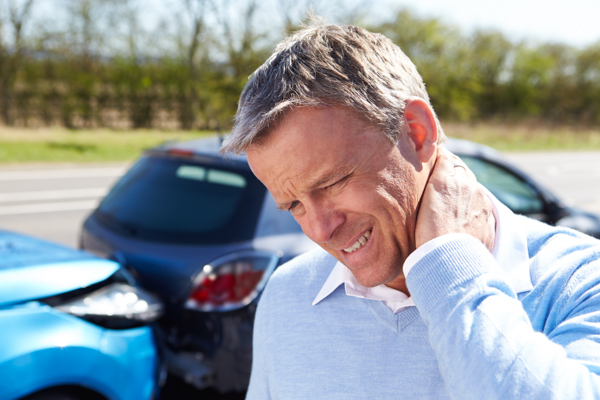
Whiplash is an injury to your neck. It is caused by your neck bending forcibly forward and then backward, or vice versa. The injury, which is poorly understood, usually involves the muscles, discs, nerves, and tendons in your neck.
What causes a whiplash?
Most whiplash injuries result from a collision that includes sudden acceleration or deceleration. Many whiplash injuries occur when you are involved in a rear-end automobile collision. They also happen as a result of a sports injury, particularly during contact sports.
What are the symptoms of a whiplash?
These are the most common symptoms of whiplash:
- Neck pain
- Neck stiffness
- Shoulder pain
- Low back pain
- Dizziness
- Pain in your arm or hand
- Numbness in your arm or hand
- Ringing in your ears
- Blurred vision
- Concentration or memory problems
- Irritability
- Sleeplessness
- Tiredness
The symptoms of whiplash may look like other conditions and medical problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is a whiplash diagnosed?
Along with a complete medical history and physical exam, tests for whiplash may include the following. Many whiplash injuries include damage to soft tissue that can’t be seen on X-rays:
- X-ray. Electromagnetic energy beams produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Large magnets and a computer make detailed images of organs and soft tissue structures in your body.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan. X-rays and computer technology make horizontal, or axial, images (often called slices) of your body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of your body, including your bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
How is a whiplash treated?
Your healthcare provider will determine specific treatment for whiplash, based on:
- Your age, overall health, and medical history
- Extent of your injury
- Your tolerance for specific medicines, procedures, or therapies
- Expectations for the course of your injury
- Your opinion or preference
Treatment may include:
- Ice applications for the first 24 hours
- Cervical (neck) collar
- Gentle, active movement after 24 hours
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs such as ibuprofen)
- Muscle relaxing medicines
- Physical therapy
- Osteopathic manipulation
What are the complications of a whiplash injury?
While most people who have a whiplash injury recover within a few weeks to a few months, some have persistent pain for several months or longer.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
If your symptoms have not improved within the time frame your healthcare provider suggested, let him or her know. Also, if your symptoms get worse or you get new symptoms, tell your provider.
Key points about whiplash
- Whiplash injury is poorly understood, but usually involves the muscles, discs, nerves, and tendons in your neck.
- It is caused by the neck bending forcibly forward and then backward, or vice versa.
- Many whiplash injuries occur if you are involved in a rear-end automobile collision.
- Your healthcare provider will determine specific treatment for your whiplash.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
- Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
- Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
- Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
- At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
- Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are.
- Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
- Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
- Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
- If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
- Know how you can contact your provider if you have questions.