Meniscus Injury Treatment
Meniscus Tear Doctors in Kenosha & Burlington, WI
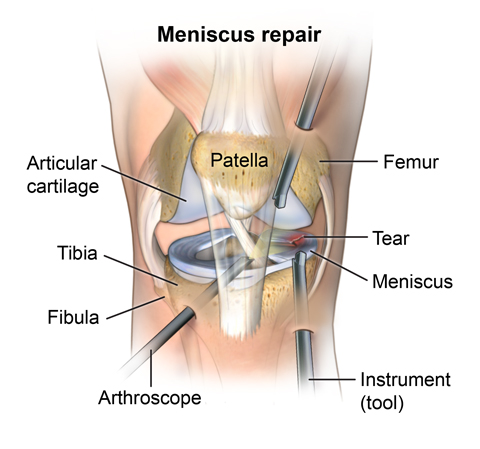
What is a torn meniscus?
There are 3 bones in the knee, the femur, tibia and patella. The ends of those bones are covered with cartilage (a smooth material that cushions the bone and allows the joint to move easily without pain). The cartilage acts as a shock absorber. Between the bones of the knees are two crescent-shaped discs of connective tissue, called menisci, which also act as shock absorbers to cushion the lower part of the leg from the weight of the rest of the body.
What causes a torn meniscus?
How is a torn meniscus diagnosed?
How is a torn meniscus treated?
What are the complications of a torn meniscus?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most common ligaments to be injured. The ACL is often stretched and/or torn during a sudden twisting motion (when the feet stay planted one way, but the knees turn the other way). Skiing, basketball, and football are sports that have a higher risk of ACL injuries.
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is also a common ligament to become injured in the knee. However, the PCL injury usually occurs with sudden, direct impact, such as in a car accident or during a football tackle.
What are the symptoms of a torn meniscus?
The following are the most common symptoms of a torn meniscus. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- Pain, especially when holding the knee straight
- Swelling and stiffness
- Knee may click or lock
- Knee may feel weak
The symptoms of a torn meniscus may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your doctor for a diagnosis.
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, diagnostic procedures for a torn meniscus may include the following:
- X-ray. A diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle.
- Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope) which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen. They are used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint. The procedure also may detect bone diseases and tumors as well as determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
Specific treatment for a torn meniscus will be determined by your doctor based on:
- Your age, overall health, and medical history
- Extent of the injury
- Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, and therapies
- Expectation for the course of the injury
- Your opinion or preference
Treatment may include:
- Icing
- Medication to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, such as ibuprofen
- Muscle-strengthening exercises
- Arthroscopic surgery
When should I call my health care provider?
Call your health care provider if your knee:
- Locks or catches or makes a clicking, popping, or grinding sound
- Is painful and swollen
- Feels week or buckles

Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your health care provider:
-
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
-
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
-
At the visit, write down the names of new medicines, treatments, or tests, and any new instructions your provider gives you.
-
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
-
Know how you can contact your provider if you have questions.



