ACL Injury Treatment
ACL Injury Doctors in Kenosha & Burlington, WI
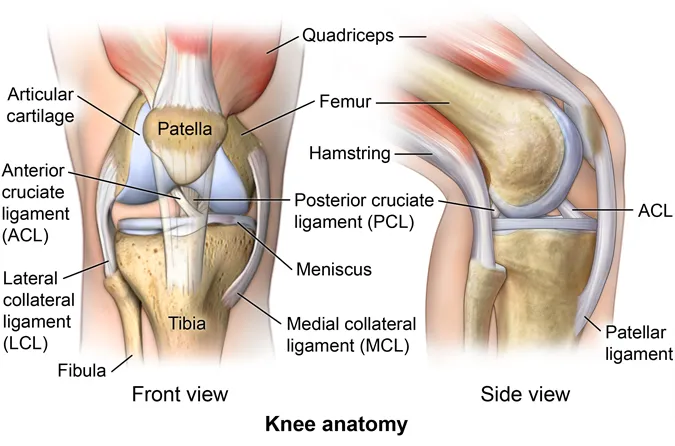
What Ligament Injuries Happen to the Knee?
There are 4 major ligaments in the knee. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and provide stability and strength to the joint. The 4 main ligaments in the knee connect the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shin bone), and include:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ligament, located in the center of the knee, that controls rotation and forward movement of the tibia (shin bone).
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). The ligament, located in the back of the knee, that controls backward movement of the tibia (shin bone).
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL). The ligament that gives stability to the inner knee.
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The ligament that gives stability to the outer knee.
How do ACL injuries occur?
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
How is a knee ligament injury diagnosed?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most common ligaments to be injured. The ACL is often stretched and/or torn during a sudden twisting motion (when the feet stay planted one way, but the knees turn the other way). Skiing, basketball, and football are sports that have a higher risk of ACL injuries.
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is also a common ligament to become injured in the knee. However, the PCL injury usually occurs with sudden, direct impact, such as in a car accident or during a football tackle.
Often, a cruciate ligament injury does not cause pain. Instead, the person may hear a popping sound as the injury occurs, followed by the leg buckling when trying to stand on it, and swelling. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
The symptoms of a cruciate ligament injury may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see your doctor for a diagnosis.
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, diagnostic procedures for a knee ligament injury may include:
- X-ray. A diagnostic test that uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film to rule out an injury to bone instead of, or in addition to, a ligament injury.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in bones and a surrounding ligament or muscle.
- Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope) that is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen; used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint; to detect bone diseases and tumors; to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.

Treatment for knee ligament injuries
Treatment may include:
-
Medicine such as ibuprofen
-
Muscle-strengthening exercises
-
Protective knee brace (for use during exercise)
-
Ice pack application (to reduce swelling)
-
Surgery



